DNA analysis shows us that the Sumatran tiger became separated from other tiger species when a rise in sea level occurred at the “Pleistocene” and “Holocene” border, approximately 12,000 to 6,000 years ago. Consequently, the Sumatran tiger was isolated from other species, enabling it to form into a unique group of closely related species. As is mentioned in the “Evolutionary History” section of this website, Sumatran tigers descended from Proailurus cats, who originated from Germany, Spain, and Mongolia. Although tigers have a vast habitat-range, (historically ranging from Turkey through South and Southeast Asia, and the eastern parts of Asia; now they are found only in places such as: South and Southeast Asia, China, and the far east of Russia), the endangered Sumatran tiger species are only found on the island of Sumatra. Tigers inhabit habitats such as Tropical rainforests, evergreen forests, woodlands, grasslands, savannas, mangrove swamps, and rocky country.
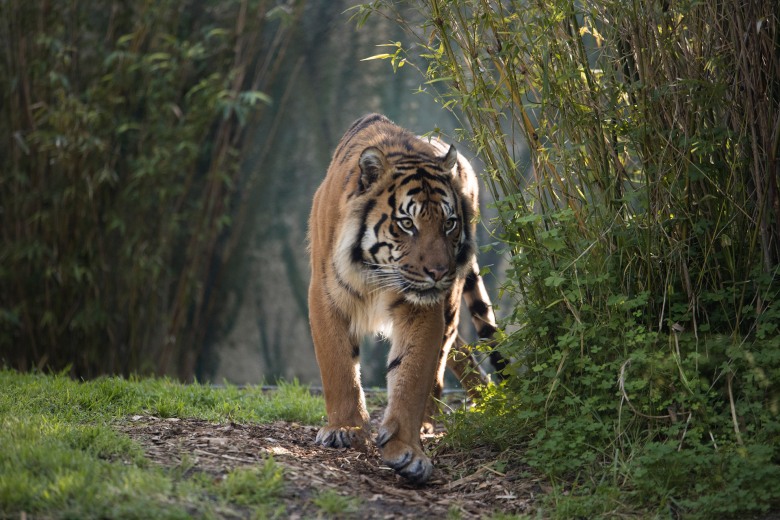

The Sumatran tiger belongs to one Biome: the Tropical rainforest. Tropical rainforests are known for their incredible biodiversity. They are located near the equator. Typically only two seasons occur in a Tropical rainforest: (rainy, and dry seasons). Important indicator species from the Tropical rainforest Biome include: Gorillas, 2-toed sloths, Orangutans, and Spider Monkeys.
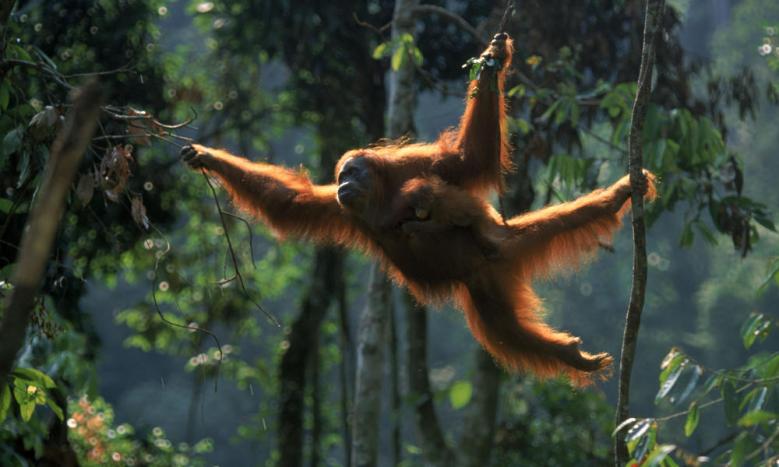
The Sumatran Lowland Rain Forests, which the Sumatran tiger inhabits, are some of the most diverse forests in the world and are also some of the most critically endangered. Sumatran forests are home to flowering plants such as: Rafflesia arnoldii, which produce the biggest flower in the world, (up to 1 meter wide!). Over 450 birds can be found in the habitat that the Sumatran tigers inhabit. Also found are figs — there are more than 100 fig species in Sumatra! Some animals that inhabit Sumatra are organisms such as: orangutans, pygmy elephants, and Sumatran rhinos.

The Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage site. This consists of three national parks: Gunung Leuser National Park, Kerinci Seblat National Park and Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park. The rainforest has the ability to preserve the majority of biota found on Sumatra, and endangered species, because it is so biodiverse, and dense. This area is inhabited by 10,000 plant species, over 200 mammal species, 580 bird species, and many more species. Sumatra is home to one of the most biodiverse Tropical rainforests in the world, covering a total area of more than Texas!

The temperature in Tropical rainforests ranges from 20-25 degrees celsius, (68-77 degrees Fahrenheit). This number varies throughout the year. The temperature average of the warmest months and the temperature average of the coldest months differs by a maximum of 5 degrees celsius. Annually, the temperature average is 68 degrees Fahrenheit and above.
Rainfall is distributed equally throughout the year. Annual rainfall levels don’t usually exceed 79 inches of rainfall.

So cool, Alex! I learned so much about the Sumatran Tiger
LikeLike